Vinegar Formula: CH₃COOH Demystified
Vinegar is a staple in kitchens and labs worldwide, but its chemical identity is often misunderstood. While vinegar is a diluted solution of acetic acid (5–20%) in water, its core formula is CH₃COOH—the molecular blueprint for acetic acid. Here’s a deep dive into its chemistry, properties, and real-world applications.
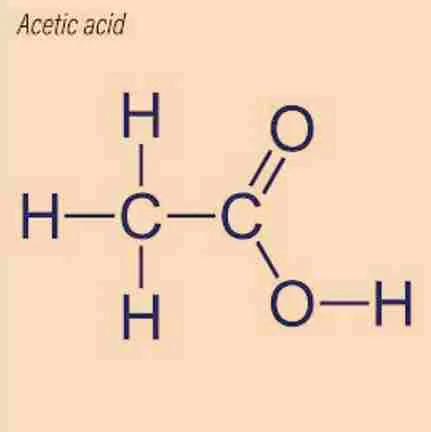
Why Is Vinegar’s Formula the Same as Acetic Acid?
Vinegar isn’t a pure compound but a mixture of water, acetic acid, and trace chemicals (like flavorings). However, acetic acid (CH₃COOH) is its active ingredient, making the formula CH₃COOH synonymous with vinegar.
Chemical and Structural Formula of Vinegar
Molecular Formula
- CH₃COOH or C₂H₄O₂
- Molar Mass: 60.052 g/mol
Structural Formula
Acetic acid consists of:
- A methyl group (CH₃) bonded to a carboxyl group (COOH).
- A double-bonded oxygen (O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the second carbon.
Key Physical Properties of Acetic Acid
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | ~1.05 g/cm³ (pure) |
| Melting Point | 16.6°C (61.9°F) |
| Boiling Point | 118.1°C (244.6°F) |
| pH (Vinegar) | 2–3 (highly acidic) |
How Vinegar’s Formula Impacts Its Uses
- Cooking:
- CH₃COOH reacts with baking soda (NaHCO₃) to release CO₂, making baked goods rise.
- Pickling: Acidity inhibits bacterial growth.
- Cleaning:
- Dissolves mineral deposits (e.g., limescale) due to its polar carboxyl group.
- Health:
- Diluted acetic acid may help regulate blood sugar (studies ongoing).
Types of Vinegar & Their Acetic Acid Content
| Type | Acetic Acid Concentration | Source |
|---|---|---|
| White Vinegar | 5–10% | Fermented ethanol |
| Apple Cider | 5–6% | Fermented apple juice |
| Balsamic | 6% (traditional) | Grape must |
FAQs: Answering Top Searches
Q: Is vinegar just diluted acetic acid?
A: Yes! Household vinegar contains 5–10% acetic acid + water.
Q: Why does vinegar smell strong?
A: The carboxyl group in CH₃COOH releases volatile acidic vapors.
Q: Can I write vinegar as C₂H₄O₂?
A: Technically yes, but CH₃COOH is preferred to show the functional group.
Q: Is vinegar safe to consume?
A: In small doses—its acidity can erode tooth enamel or irritate the stomach if overused.
Key Takeaways
- Core Formula: Vinegar = CH₃COOH (acetic acid) + H₂O.
- Functionality: The carboxyl group (-COOH) drives its acidic behavior.
- Uses: From cooking to cleaning, vinegar’s chemistry makes it versatile.
- Read Also:
- Greater Than and Less Than Symbols
Admin at Sirfal.com – Experienced blogger since 2015, sharing Q&A content and latest job updates.